Container Management
Containers are the core concept of Docker, being running instances of images. Through the container management page, you can create, start, stop, and manage containers.
Container List
Go to the Container page, which displays the container list by default.
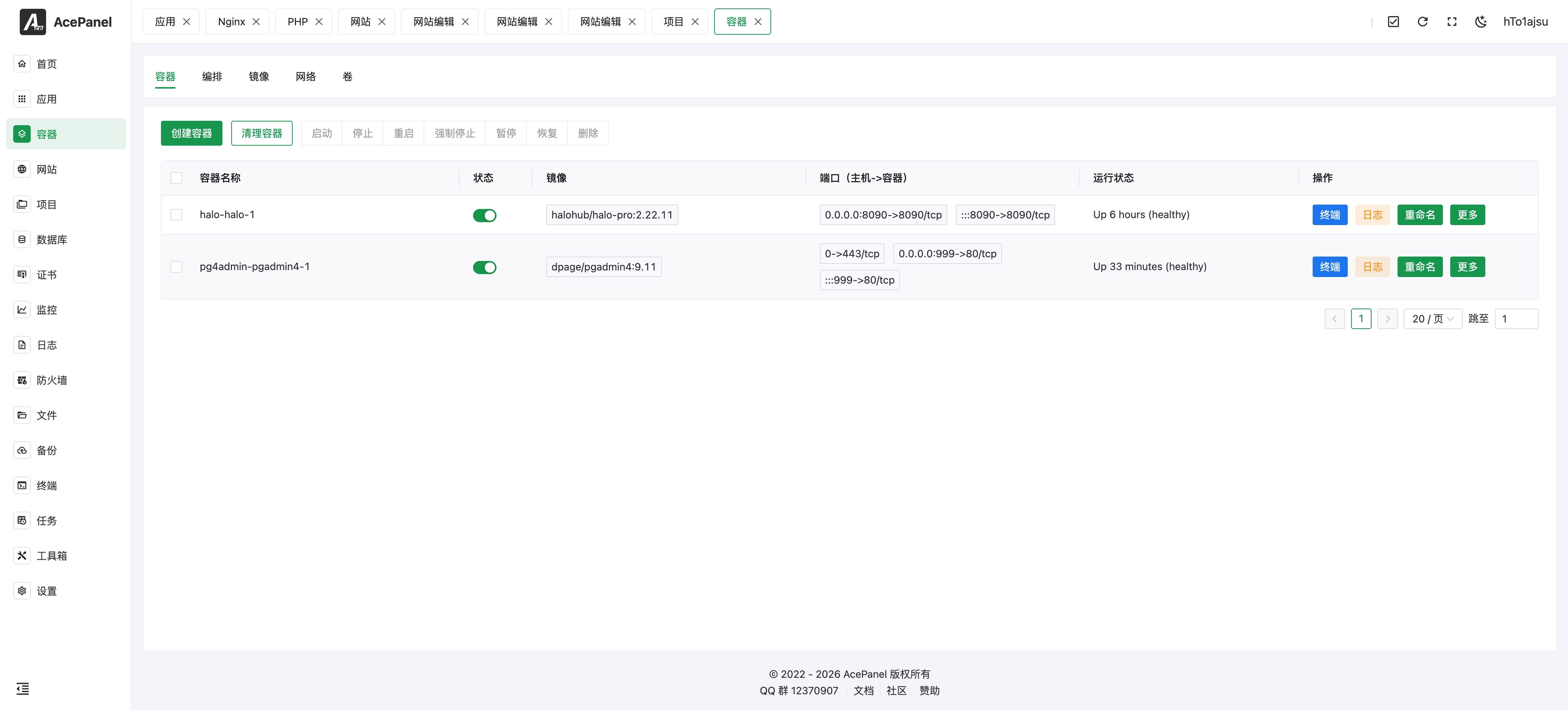
The list displays the following information:
- Container Name: Name of the container
- Status: Running status switch
- Image: Image used by the container
- Ports: Port mapping (host port -> container port)
- Running Status: Detailed running status information
- Actions: Terminal, logs, rename, etc.
Create Container
Click the Create Container button to open the creation dialog.
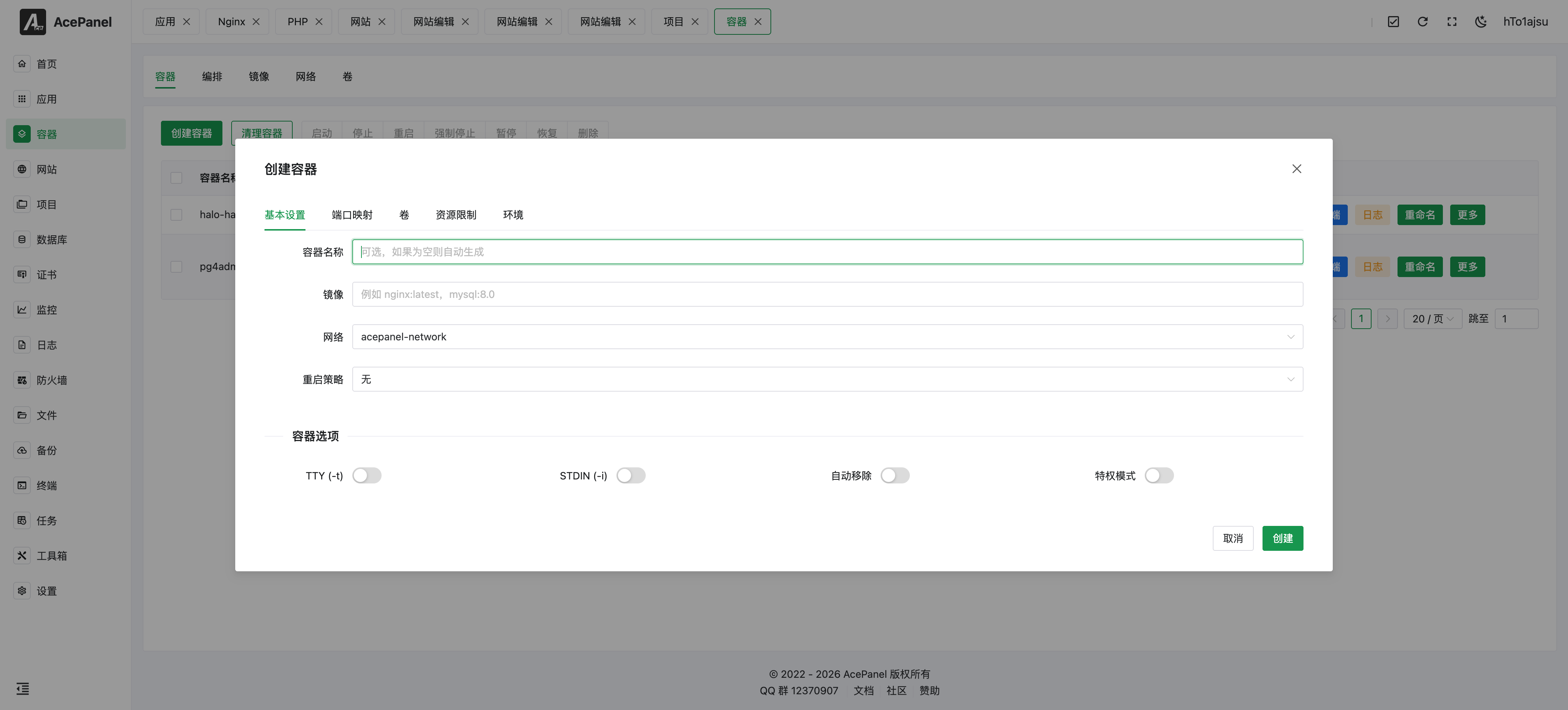
Basic Settings
- Container Name: Optional, auto-generated if left empty
- Image: Docker image name, e.g.,
nginx:latest,mysql:8.0 - Network: Select the network for the container to use
- Restart Policy: Restart behavior after container exits
- None: Do not auto restart
- always: Always restart
- on-failure: Restart on failure
- unless-stopped: Restart unless manually stopped
Advanced Options
- TTY (-t): Allocate a pseudo-TTY
- STDIN (-i): Keep STDIN open
- Auto Remove: Automatically delete container when stopped
- Privileged Mode: Grant container full system privileges (use with caution)
Port Mapping
Map container internal ports to host ports, format: host_port:container_port
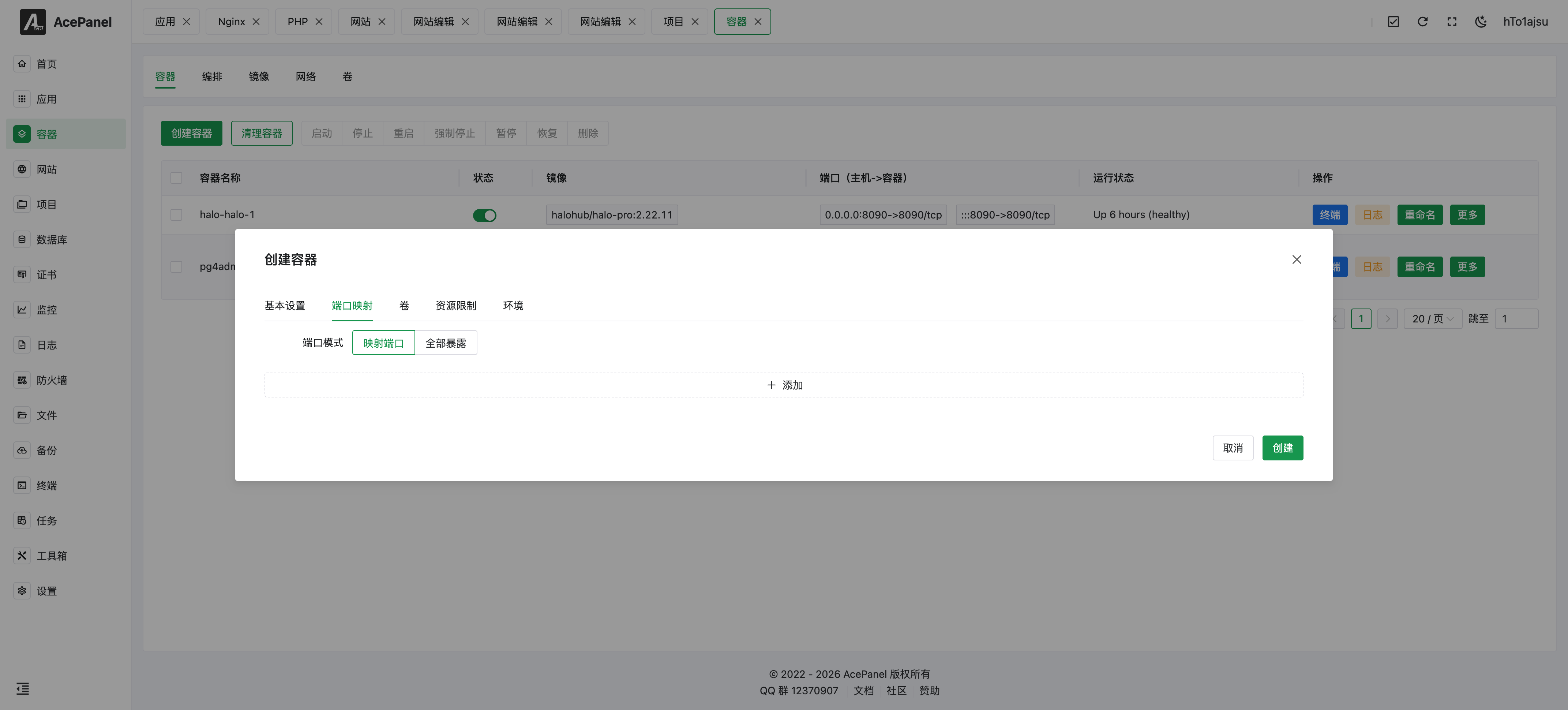
For example: 8080:80 means mapping container port 80 to host port 8080.
Volume Mounts
Mount host directories or data volumes to the container, format: host_path:container_path
For example: /opt/ace/data:/data means mounting the host's /opt/ace/data directory to the container's /data directory.
Resource Limits
Limit the CPU and memory resources the container can use.
Environment Variables
Set container environment variables, format: KEY=VALUE
Container Operations
Batch Operations
After selecting multiple containers, you can perform batch operations:
- Start: Start selected containers
- Stop: Stop selected containers
- Restart: Restart selected containers
- Force Stop: Force stop selected containers
- Pause: Pause selected containers
- Resume: Resume paused containers
- Delete: Delete selected containers
Single Container Operations
- Terminal: Open the container's terminal to execute commands inside the container
- Logs: View container runtime logs
- Rename: Modify container name
- More: View details, export, and other operations
Clean Containers
Click Clean Containers to delete all stopped containers and free up system resources.
Note
The cleanup operation cannot be undone. Please ensure stopped containers are no longer needed.
