Container
The container module provides complete Docker container management functionality, including management of containers, compose, images, networks, and volumes.
Prerequisites
Before using the container feature, you need to install Docker or Podman first:
- Go to Applications > Native Applications
- Find Docker or Podman, click Install
Feature Overview
The container module is divided into five parts:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Container | Manage running container instances |
| Compose | Manage multi-container applications using Docker Compose |
| Image | Manage local images |
| Network | Manage Docker networks |
| Volume | Manage data volumes |
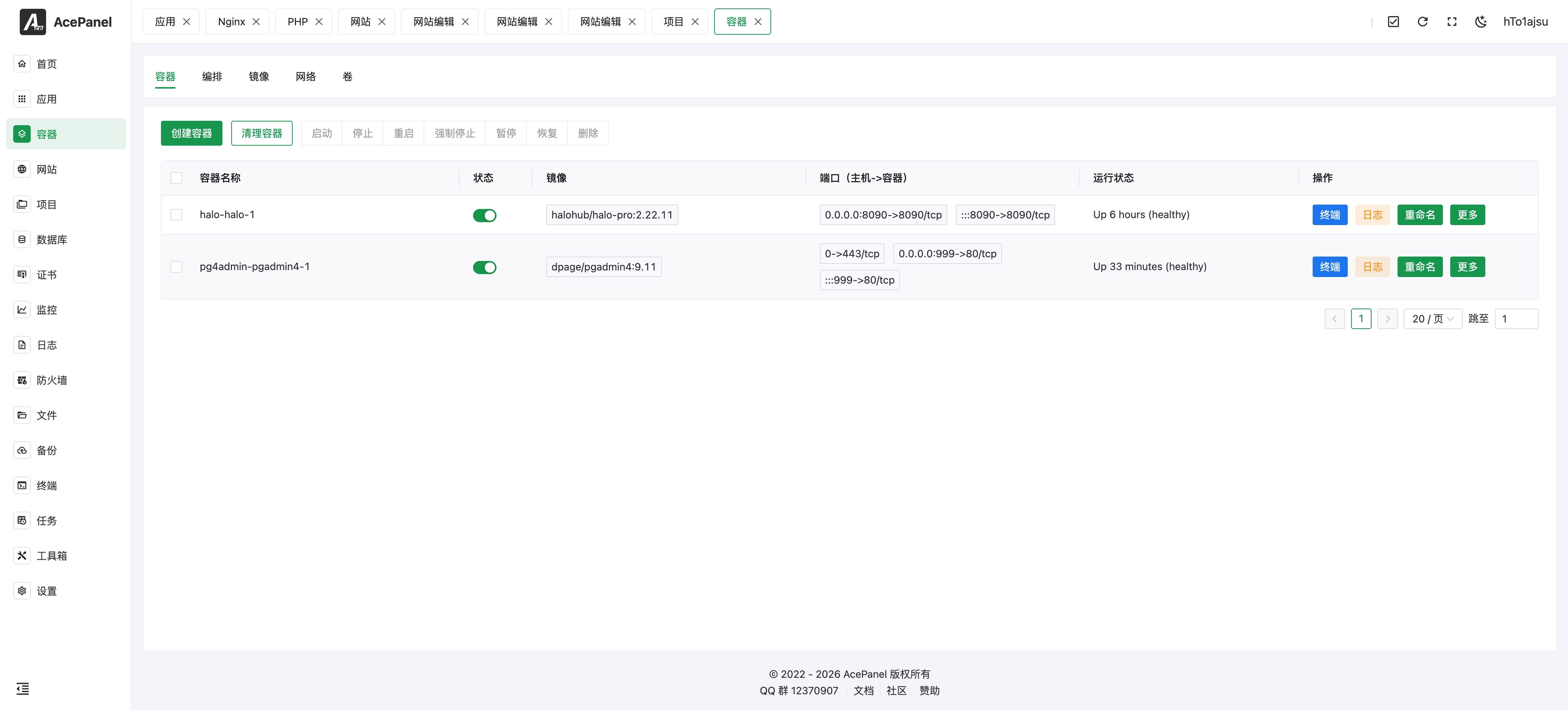
Quick Start
Create Container
- Go to the Container page
- Click Create Container
- Enter the image name (e.g.,
nginx:latest) - Configure port mapping, volume mounts, etc.
- Click Create
Use Container Templates
If you want to quickly deploy common applications, it is recommended to use Container Templates, which allows one-click deployment without manual configuration.
Container vs Native Application
| Feature | Container | Native Application |
|---|---|---|
| Isolation | Fully isolated | Shared system environment |
| Performance | Slight overhead | Native performance |
| Deployment | Standardized, portable | Depends on system environment |
| Resource Usage | Higher | Lower |
| Version Management | Easy to switch | Requires manual management |
Next Steps
- Container Management - Learn how to manage containers
- Compose Management - Learn how to use Docker Compose
- Image Management - Learn how to manage images
- Network Management - Learn how to manage networks
- Volume Management - Learn how to manage data volumes
