User Management
The user management page is used to create and manage database users and set user permissions.
User List
Go to Database > User tab to view the user list.
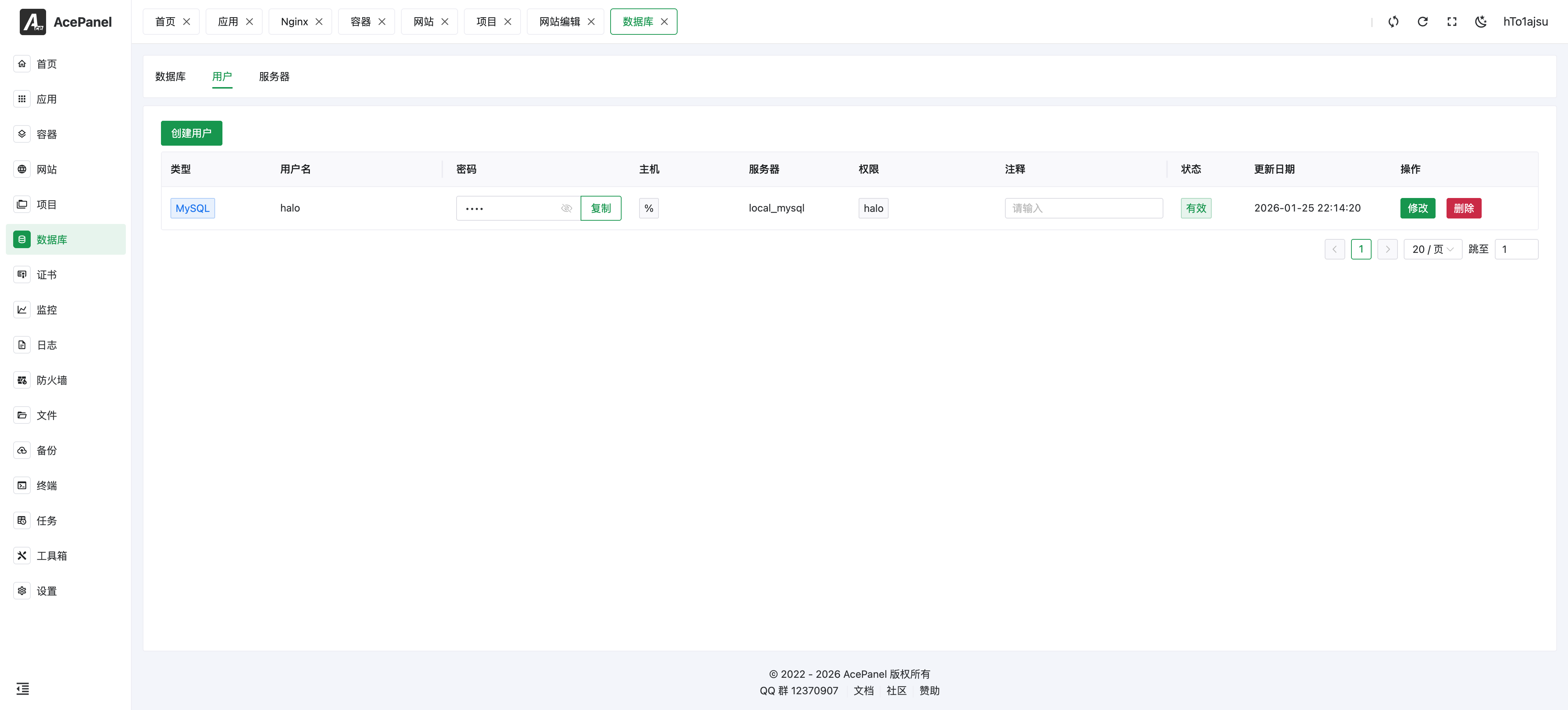
The list displays the following information:
- Type: Database type
- Username: Database username
- Password: User password (click to copy)
- Host: Allowed connection hosts
- Server: The database server it belongs to
- Permissions: Databases the user has permissions for
- Comment: Remarks
- Status: User status
- Update Date: Last update time
- Actions: Modify, delete
Create User
- Click the Create User button
- Fill in the configuration:
- Server: Select database server
- Username: Database username
- Password: User password (strong password recommended)
- Host: Allowed connection host address
- Permissions: Select databases the user can access
- Click Create
Host Settings
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
localhost | Only allow local connections |
127.0.0.1 | Only allow local IP connections |
% | Allow connections from any host |
192.168.1.% | Allow connections from specified subnet |
192.168.1.100 | Only allow connections from specified IP |
Security Notice
Production environments are not recommended to use % to allow connections from any host. Should be restricted to specific IP addresses or subnets.
Modify User
Click the Modify button on the right side of the user to:
- Modify password
- Modify allowed connection hosts
- Modify database permissions
Delete User
Click the Delete button on the right side of the user to delete the user.
Note
After deleting a user, applications using that user to connect to the database will not work properly.
Permission Explanation
Percona/MySQL/MariaDB Permissions
When creating a user, you can select databases to grant permissions:
- Select specific databases: User can only access selected databases
- No selection: User has no database permissions
PostgreSQL Permissions
PostgreSQL permission management is more fine-grained. You can set different permissions for databases, schemas, tables, etc. The panel only supports granting database access permissions.
Password Security
- Use strong passwords containing uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters
- Password length recommended 16 characters or more
- Use different database users for different applications
- Change passwords regularly
