Webhook
Webhooks allow you to trigger script execution on the server through HTTP requests, enabling automated deployment, CI/CD integration, and other features.
Create Webhook
Click the Create Webhook button and fill in the following information:
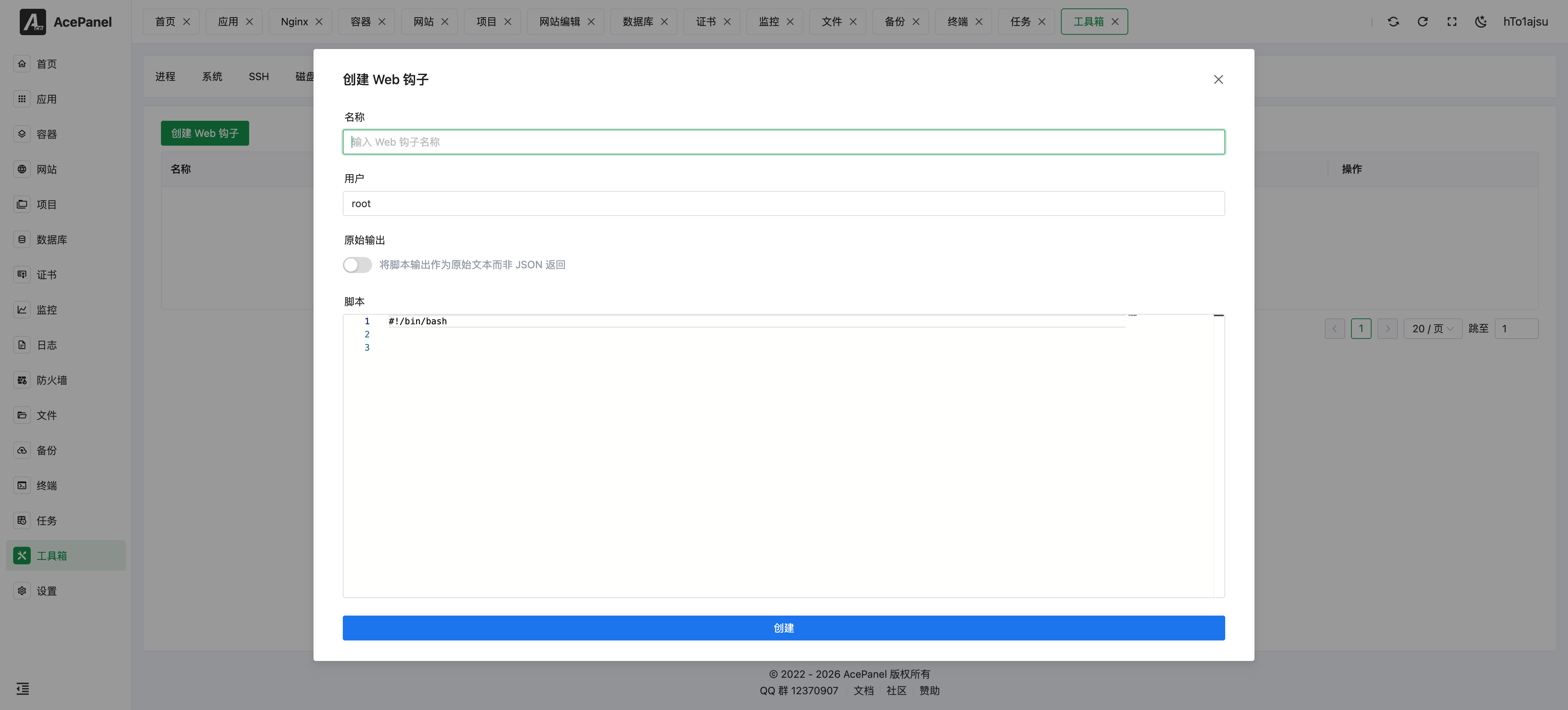
- Name: The name of the webhook, used to identify its purpose
- User: The system user that executes the script, default is root
- Raw Output: When enabled, returns the raw output of the script; when disabled, returns JSON format
- Script: The Shell script content to execute
Usage
After creation, the system will generate a unique Key. Access the following URL to trigger script execution:
https://your-panel-domain/api/webhook/{key}Supports both GET and POST requests.
Use Cases
Git Auto Deployment
Combined with GitHub/GitLab Webhook functionality, achieve automatic deployment after code push:
bash
#!/bin/bash
cd /opt/ace/projects/myproject
git pull origin main
npm install
npm run buildScheduled Task Trigger
Trigger specific operations through external services (such as monitoring systems):
bash
#!/bin/bash
# Clean temporary files
rm -rf /tmp/cache/*
# Restart service
systemctl restart myappCI/CD Integration
Call Webhook in CI/CD pipeline to complete deployment:
bash
# In CI script
curl -X POST https://panel.example.com/api/webhook/your-keyList Description
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | Webhook name |
| Key | Unique identifier, used to build the call URL |
| Run User | System user that executes the script |
| Raw Output | Whether to return raw text output |
| Enabled | Whether the webhook is enabled |
| Call Count | Cumulative number of calls |
| Last Call | Last call time |
Notes
- The Key is sensitive information, do not disclose it to untrusted people
- Scripts are executed as the specified user, pay attention to permission control
- It is recommended to add necessary error handling in scripts
- You can temporarily disable a webhook using the disable switch
